Interesting Facts
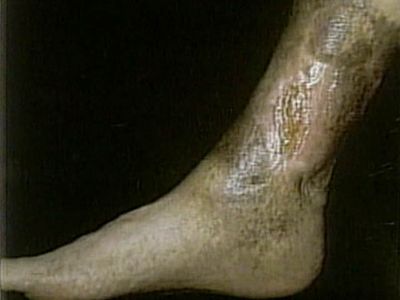
While MRSA is becoming more common in the United States, very few people know very much about this infection. Here are some interesting facts that explain a little bit more about this infection and how common it is.
To diagnose MRSA in a person, a sample of the patient's skin, pus, blood, urine, or tissue is taken to a lab where it is cultured for Staphylococcus aureus. Once it is cultured, it grown in a petri dish and exposed to several different types of antibiotics, methicillin being one of them. If the bacteria is able to grow in the presence of methicillin, the patient is diagnosed with MRSA. (www.medicinenet.com)
While this is the most accurate way of diagnosing MRSA, it is by no means the fastest. In 2008 the United States FDA approved a blood test that can tell if you have MRSA in as little as two hours by being able to detect Staphylococcus aureus DNA in the blood. While this test may be faster, it should not be the only test done. It is commonly used in patients that have already been diagnosed with the infection and doctors need to check on it to gauge the progress of the infection. (www.medicinenet.com)
The Kaiser foundation found that in 2007, 1.2 million hospital patients were diagnosed with MRSA. That is about 10 times higher than originally thought. The mortality rate among these people was 4-10%. In general, if a MRSA infection is taken care of properly, the patient shouldn't die from the infection. (www.medicinenet.com)
The people who are at greatest risk of MRSA are any people in hospitals or other healthcare facilities such as nursing homes. It is also most commonly found in people over the age of 65. While MRSA in hospitals or other healthcare settings are the most common, MRSA can also occur in healthy people who have no recent history of hospitalization or any type of medical procedure. (www.medicinenet.com)
MRSA has been found in many hospitals, nursing homes, schools, and prisons throughout the country (Osborne, 2008).
It is also thought that about 30% of the general population (Harvard Women's Health, 2008) are colonized by Staphylococcus aureus. If you are colonized by Staphylococcus aureus, it is another way of saying that you are a carrier. You have the bacteria on your body, but it is not causing an infection.
MRSA is now believed to cause 64% of Staph infections (Harvard Women's Health, 2008).
In 2005, 95,000 people in the US had an invasive MRSA infection (Consumer Reports, 2008). 14% of these people are believed to have gotten the infection in the community because they were not in a healthcare setting (Consumer Reports, 2008).
I worked in a nursing home for a summer and I personally had to take care of people who had MRSA. We had to wear gowns that covered our arms and everything except for our face. This is to make sure that MRSA is not passed on to any of the staff or any other patient. MRSA are also put into isolation so that they don't pass the infection onto their healthy roommate or anyone else.
seubert.heid@students.uwlax.edu